Cancer, a word that strikes fear and uncertainty into the hearts of many. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricate world of cancer, equipping you with knowledge to navigate this challenging journey. From understanding the fundamentals of cancer to discussing risk factors, early detection, treatment options, and emotional support, we’ll leave no stone unturned.
Navigating Cancer: Your Comprehensive Guide 2023

I. Introduction
Definition and Overview of Cancer
Disease, at its center, is an uncontrolled development of strange cells inside the body. It can appear in different structures and influence various organs and tissues. Understanding its starting points and suggestions is significant.
Importance of a Comprehensive Guide
A comprehensive guide to cancer is not just informative; it’s empowering. With knowledge comes the ability to make informed decisions about your health and treatment options.
II. Understanding Cancer
The Origin of Cancer Cells
Genetic Mutations
One of the primary factors contributing to cancer is genetic mutations. These alterations in DNA can lead to the unchecked proliferation of abnormal cells, the hallmark of cancer.
Environmental Factors
In addition to genetics, environmental factors such as exposure to carcinogens and radiation can play a pivotal role in the development of cancer.
Types of Cancer
Cancer is not a one-size-fits-all disease. It can be categorized into various types, each with its unique characteristics and treatment approaches.
Carcinomas
Carcinomas are cancers that originate in epithelial tissues, which cover the body’s surfaces and line internal organs.
Sarcomas
Sarcomas develop in the body’s connective tissues, such as bones, muscles, and cartilage.
Leukemias
Leukemias are cancers of the blood and bone marrow, leading to an overproduction of abnormal white blood cells.
Lymphomas
Lymphomas affect the lymphatic system, which plays a crucial role in the body’s immune response.
Read More Articles :- hrhealthtips.com
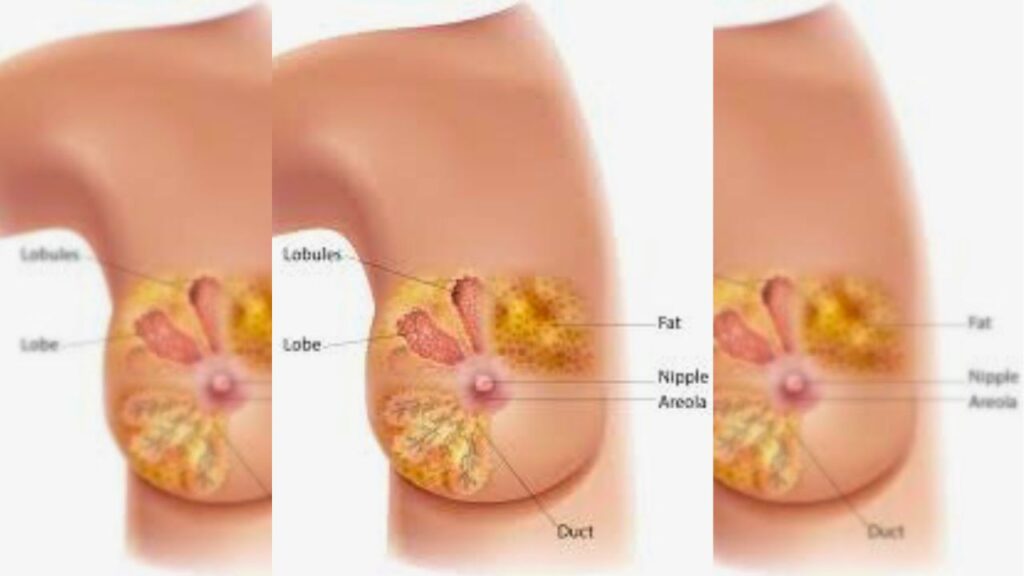
III. Risk Factors
Genetics
Hereditary Factors
A few people are hereditarily inclined toward malignant growth because of acquired transformations. Understanding your hereditary gamble can direct preventive measures.
Genetic Testing
Advancements in genetic testing allow for the identification of specific mutations that increase cancer susceptibility.
Lifestyle Choices
Smoking and Tobacco Use
Tobacco use remains a leading cause of preventable cancer deaths. Quitting is the best prevention strategy.
Diet and Nutrition
Dietary choices can influence cancer risk. A balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables can provide protective benefits.
Physical Activity
Maintaining a physically active lifestyle can reduce the risk of certain cancers.
Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption is linked to an increased risk of various cancers. Moderation is key.
Environmental Exposures
Carcinogens
Exposure to carcinogens, substances capable of causing cancer, should be minimized whenever possible.
Radiation
Prolonged exposure to ionizing radiation, such as from X-rays or nuclear fallout, can raise cancer risk.
Workplace Hazards
Certain occupations carry a higher risk of exposure to cancer-causing agents. Occupational safety measures are crucial.

Read More Articles :- hrhealthtips.com
IV. Early Detection
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early detection can significantly improve cancer outcomes by allowing for timely intervention.
Screening Methods
Mammograms
Mammograms are essential for the early detection of breast cancer in women.
Pap Smears
Pap smears are crucial in detecting cervical cancer in its early, highly treatable stages.
Colonoscopies
Colonoscopies are recommended for the early detection of colorectal cancer, which can be asymptomatic in its initial stages.
Warning Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing common and less recognized symptoms can prompt early medical evaluation.
Diagnostic Tests
Biopsies and various imaging techniques are essential for confirming a cancer diagnosis.
This comprehensive guide will continue to explore cancer staging, treatment options, integrative approaches, and many other crucial aspects of navigating the challenging terrain of cancer. Stay tuned as we delve deeper into each facet of this journey, offering you guidance and support every step of the way.
V. Cancer Staging
TNM System
Cancer staging provides a standardized way to describe the extent of cancer within the body. The TNM system, which stands for Tumor, Nodes, and Metastasis, is commonly used for this purpose. It assesses the size of the primary tumor (T), the involvement of nearby lymph nodes (N), and the presence of metastasis (M).
Stages 0 to IV
Cancer is categorized into stages, ranging from 0 to IV, with each stage representing the progression of the disease. The stage determines the treatment approach and prognosis.
Implications for Treatment
The stage of cancer often dictates the choice of treatment. Early-stage cancers may be treated with localized therapies, while advanced stages may require more aggressive interventions.
VI. Treatment Options
Surgery
Surgery involves the removal of the cancerous tumor or tissue. It is often the initial step in cancer treatment and can be curative for some early-stage cancers.
- Types of Surgeries
- Lumpectomy: Removal of a small portion of the breast containing the tumor.
- Mastectomy: Complete removal of the breast tissue.
- Tumor Resection: Excision of the tumor from organs or tissues.
- Lymph Node Dissection: Removal of lymph nodes to assess cancer spread.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to target and destroy cancer cells. It can be employed as a standalone treatment or in combination with other therapies.
- External Beam
- External radiation is delivered from a machine outside the body, precisely targeting the tumor.
- Internal Radiation
- Internal radiation involves placing a radioactive source directly inside or near the tumor.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy utilizes drugs to inhibit the growth and spread of cancer cells. It can be administered orally or intravenously and is effective against a wide range of cancers.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy harnesses the body’s immune system to identify and attack cancer cells. It has shown promise in treating various types of cancer.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy uses drugs that specifically target molecules or proteins involved in the growth of cancer cells, minimizing damage to healthy cells.
Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy is commonly used to treat hormone-sensitive cancers by blocking hormone production or action.
Stem Cell Transplantation
Stem cell transplantation may be recommended for certain blood cancers and involves replacing damaged or diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells.
VII. Integrative Approaches
Complementary Therapies
Complementary therapies, such as acupuncture, massage, and yoga, can provide relief from cancer-related symptoms and enhance overall well-being.
Diet and Nutrition
Optimal nutrition can support the body during cancer treatment and recovery. Nutrient-rich foods aid in maintaining strength and immunity.
Mind-Body Practices
Mindfulness meditation, relaxation techniques, and counseling can help manage stress and emotional challenges during cancer treatment.
VIII. Managing Side Effects
Common Side Effects
Cancer treatments can lead to side effects such as fatigue, nausea, and hair loss. Understanding and addressing these symptoms is vital.
Coping Strategies
Coping strategies, including exercise, support groups, and relaxation techniques, can improve the quality of life during cancer treatment.
Supportive Care
Supportive care focuses on alleviating the physical and emotional burden of cancer treatment through palliative care and symptom management.
In our journey through this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore survivorship and follow-up care, the emotional and psychological impact of cancer, the role of caregivers, and the latest research and advancements in cancer treatment. Together, we’ll navigate the complexities of cancer, equipping you with the knowledge and resources to face this challenge head-on.
IX. Survivorship and Follow-Up
Life After Treatment
Survivorship involves adapting to life after cancer treatment, addressing physical and emotional changes, and focusing on overall well-being.
Monitoring for Recurrence
Regular follow-up appointments and monitoring are essential to detect any signs of cancer recurrence early.
Long-Term Effects
Cancer survivors may experience long-term physical and psychological effects. Understanding and managing these effects is crucial for a healthy post-treatment life.
X. Emotional and Psychological Impact
Coping with Diagnosis
The emotional impact of a cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming. Coping strategies and support are essential for mental well-being.
Mental Health Support
Psychological support, counseling, and therapy can help individuals navigate the emotional challenges of cancer.
Support Groups
Joining cancer support groups can provide a sense of community and shared experiences, reducing feelings of isolation.
XI. Caregiver’s Role
Providing Support
Caregivers play a pivotal role in supporting and assisting cancer patients throughout their journey.
Self-Care for Caregivers
Taking care of one’s own physical and emotional well-being is essential for caregivers to provide effective support.
Stay tuned for the next part of this comprehensive guide, where we’ll explore the critical aspects of cancer research and advancements, as well as prevention strategies, resources, and support available to individuals and families affected by cancer. Your path to understanding and navigating cancer continues here.
XII. Research and Advancements
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are essential for advancing cancer treatment. They test new therapies and interventions, offering hope for improved outcomes.
Promising Developments
Continual research leads to breakthroughs in cancer treatment. Stay informed about the latest developments and their potential impact on your journey.
Future of Cancer Treatment
The future of cancer treatment holds promise through personalized medicine, innovative therapies, and a deeper understanding of the disease’s intricacies.
XIII. Prevention Strategies
Lifestyle Modifications
Making healthy lifestyle choices, such as quitting smoking, maintaining a balanced diet, and staying physically active, can reduce your risk of developing cancer.
Vaccinations
Certain vaccines, like the HPV and hepatitis B vaccines, can prevent infections that are linked to cancer development.
Early Detection Programs
Participating in early detection programs and screenings can detect cancer in its earliest, most treatable stages.

XIV. Resources and Support
Organizations and Foundations
Numerous organizations and foundations are dedicated to cancer research, education, and support. They offer valuable resources and assistance.
Financial Assistance
Managing the financial burden of cancer treatment can be challenging. Explore financial assistance programs to ease the costs.
Online Communities
Online cancer communities provide a platform for connecting with others facing similar challenges. Sharing experiences and advice can be immensely helpful.
XV. Conclusion
The Journey Ahead
Your journey through the complex landscape of cancer is unique, but you are not alone. Knowledge is your greatest ally in navigating this path.
Empowerment Through Knowledge
This comprehensive guide aims to empower you with the information and support needed to face cancer head-on. By understanding the disease, treatment options, and available resources, you can make informed decisions and embrace hope on your journey to recovery.
Cancer is a formidable opponent, but armed with knowledge, a supportive network, and a resilient spirit, you can navigate its challenges with strength and determination. Stay with us as we delve deeper into each facet of this comprehensive guide, providing you with the guidance and reassurance you need. Your journey to conquer cancer continues, one step at a time.
1 thought on “Navigating Cancer: Your Comprehensive Guide 2023”